时间:2024-03-01|浏览:356
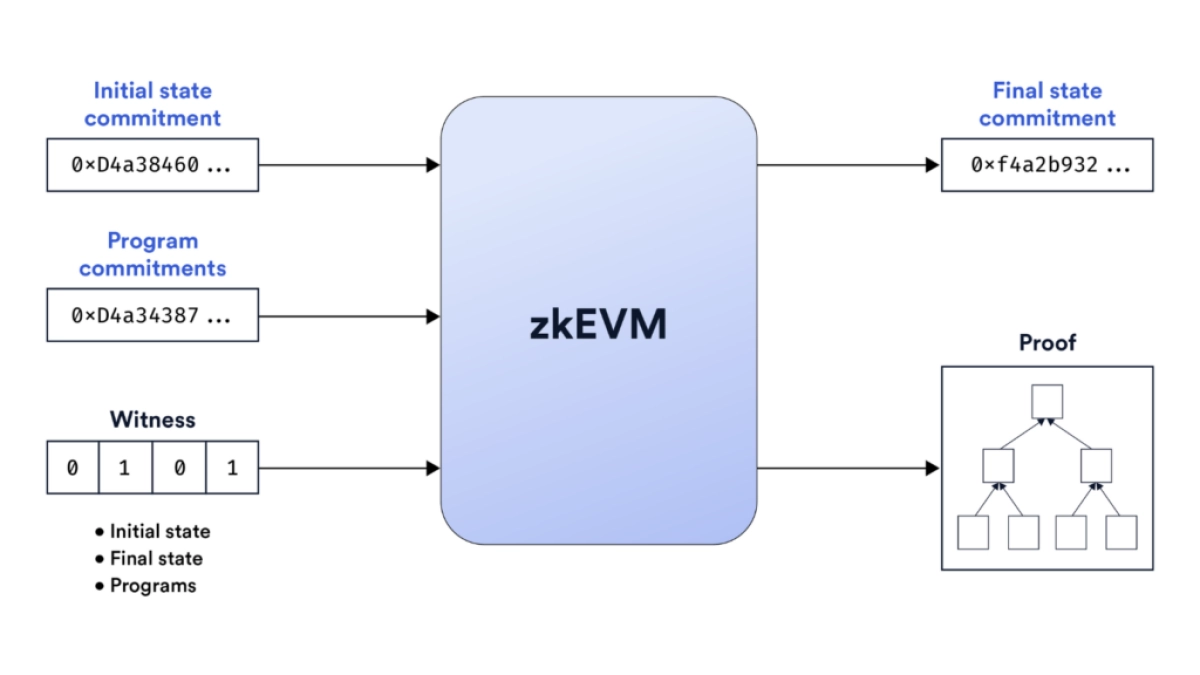
zkEVMs can validate and execute blockchain operations without needing to expose all the details. It's like saying, "I can prove this transaction or contract is valid and follows the rules, but I won't show you all the inner workings of it." Image source: Chainlink
While zkEVMs opened promising doors, they realized their potential posed major technical challenges. The EVM was never designed with proof, so several aspects conflict with this new paradigm.
For one, the EVM's stack-based architecture proved difficult to convert to a format compatible with proving. Its special opcodes for error handling also confounded efforts to build verifiable circuits.
Storage was another hurdle, as the EVM's Merkle Patricia tree clashed with proving needs. Replacing the KECCAK256 hashing function helped but risked breaking infrastructure compatibility.
Most significantly, zero-knowledge proofs demand computationally-intensive operations that drive up costs, especially on-chain. Generating and verifying proofs for each smart contract execution transaction consumed prohibitive resources.
Addressing these issues required rethinking core EVM components and sparking innovations in proofs like optimized circuits and hybrid STARK-SNARK schemes. Much progress has been made, though optimizations continue as the field matures. Perfecting zkEVMs necessitated reconciling two dissimilar yet essential technologies.
While research continues, several zkEVM systems have already launched, each approaching the technical challenges somewhat differently:
Beyond technical distinctions, these zkEVMs also vary in features, user experience optimizations, and partnership ecosystems. All represent significant milestones in proving EVM compatibility while maintaining practical usability and performance.
| Project | Approach | Target Users | Unique Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polygon Hermez | EVM-compatible, SNARK-based | DeFi protocols, DEXes | High volumes, ETH-centric |
| zkSync | EVM, SNARK-based, JAASM | DeFi, dApps, Developers | Speed, Decentralization |
| AppliedZKP | zkVM, circuits | Researchers, Builders | Security research focus |
| Matter Labs Loop | zkSNARKs, optimistic | dApps, protocols | Flexible assumptions |
Popular zkEVM Projects and Focus Areas
通过将以太坊的多功能智能合约与隐私保护扩展相协调,zkEVM 承诺为用户和开发人员带来大量好处:
更快、更便宜的交易
:通过批量在链下执行交易,zkEVM 每秒可以处理数千笔交易,而以太坊的 TPS 为 15。
天然气成本也低得多。
增强隐私
:用户无需信任中心化服务即可受益于强大的隐私,因为公共区块链上仅公开加密证明。
智能合约扩展
:dApp 能够通过第 2 层进行扩展,同时保留去中心化安全性等核心以太坊优势。
开发连续性
:开发人员利用相同的 Solidity/Vyper 语言、工具、测试框架和充满活力的以太坊生态系统。
跨链互操作性
:随着 EVM 兼容性的提高,桥有一天可能允许资产和计算无缝地穿越不同的链。
zkEVM 的广泛采用可以实现以太坊作为通用去中心化背板的愿景,第 2 层网络通过可扩展性和隐私性释放其全部潜力。
然而,在扩大这些好处方面仍然存在挑战。
现状与展望
虽然 zkEVM 在概念上取得了突飞猛进的发展,但研究和大规模广泛使用之间仍然存在主要障碍。
其中最主要的是高昂的部署成本,目前将 zkEVM 的使用限制在特定场景中并限制了总体吞吐量。
此外,与更简单的解决方案相比,将复杂的 zkEVM 证明完全集成到应用程序中会带来 UI/UX 挑战和降低开发人员生产力的风险。
然而,像 Manta 这样的项目正在努力消除这种复杂性。
展望未来,对 zkSNARKS/STARKS 构造、电路设计和完善 EVM 抽象层的持续优化有望使成本和可用性差距稳步缩小。
zkPorter 汇总聚合器等有前景的开发可能会进一步提高吞吐量。
随着 zkEVM 采用的不断增长,其他研究途径(例如减少证明大小、提供高级密码学云服务以及使用专用硬件)也值得探索。
网络之间的互操作性也仍处于萌芽阶段。
底线
尽管挑战依然存在,但 zkEVM 的进展揭示了一个未来,即使是大规模的去中心化应用程序也可以通过智能合约保持私密性、低成本和完全信任——这些目标在几年前似乎是不可想象的。
目前,早期的例子证明了这个概念的有效性。
明天等待着它们广泛、用户友好的现实。
如果您想了解有关区块链技术支持的独特计算用例的更多信息,请查看我们关于去中心化物理基础设施网络 (DePIN) 的文章。
![[斯科特]了解 zkEVM:将智能合约引入第 2 层 | 币法典](/img/20240301/3656120-1.jpg)
![[斯科特]了解 zkEVM:将智能合约引入第 2 层 | 币法典](/img/20240301/3656120-1.jpg)

![[斯科特]Flow价格上涨预测达1.81美元|币法典](/img/btc/115.jpeg)



![[加密艺术家]zkEVM:未来游戏代名词](/img/btc/54.jpeg)
![[加密艺术家]不可变的zkEVM:区块链游戏的未来代名词](/img/btc/56.jpeg)
